The paper highlighted how the platform addressed the fragmented nature of heart failure care by enabling continuous communication between hospital specialists and community healthcare providers.
Study Design and Implementation
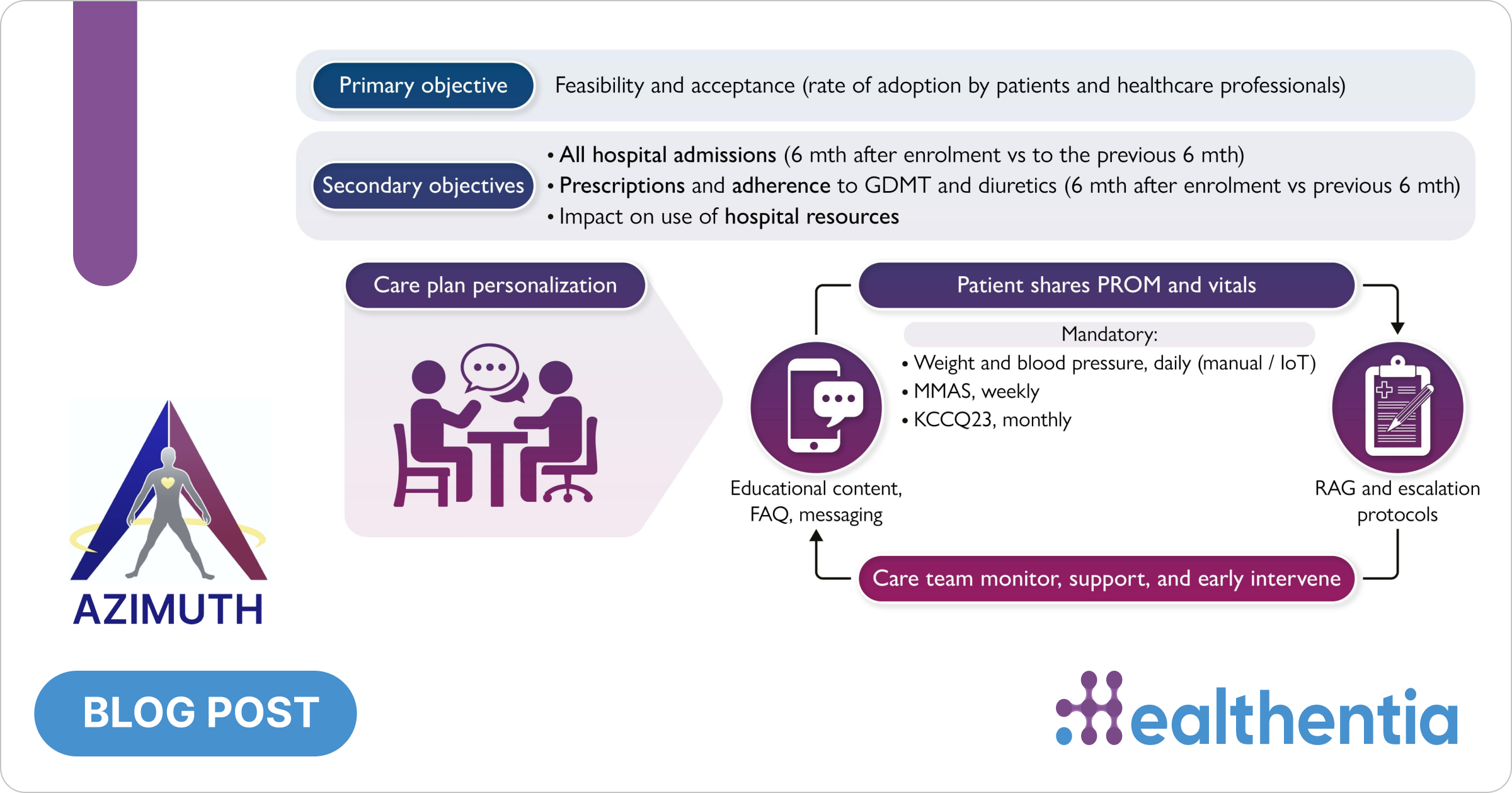
The AZIMUTH study (FondAZione A. Gemelli IRCCS Artificial Intelligence Empowered Digital PlatforM to sUpport paTients with Heart Failure) addressed this healthcare challenge through innovative digital health technology, demonstrating how smartphone-based care could transform outcomes for heart failure patients. This multicenter, prospective study enrolled 300 heart failure patients across four leading Italian medical centers in Phases 1 and 2.
The study utilized Healthentia v3, a Class I Software as Medical Device (SaMD), as the core platform for remote patient monitoring and care delivery operating through two integrated components:
Patient Mobile Application: Patients used intuitive “widgets” for daily health monitoring, including mandatory weight and blood pressure tracking, validated questionnaires (Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire and medication adherence assessments), and optional monitoring of heart rate, oxygen saturation, and physical activity. The app seamlessly integrated with Bluetooth-enabled devices to minimize manual entry errors.
Clinical Dashboard: Healthcare providers accessed a comprehensive platform that consolidated patient data into actionable insights, featuring real-time monitoring, intelligent alert systems based on clinical thresholds, longitudinal trend analysis, and integrated patient communication tools.
The study carefully addressed the real-world implementation by establishing clear inclusion criteria that balanced technological requirements with practical applicability. Patients required basic digital literacy or caregiver support, smartphone compatibility, and received comprehensive training during enrollment. The platform was designed for intuitive use across age groups, ensuring broad accessibility.
Proven Results
The study successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of digital health solutions in heart failure management:
Patient Engagement: Achieved the primary objective with over 70% of patients successfully engaging with the digital platform throughout the study period.
Clinical Improvements: Patients showed significantly improved medication adherence and treatment engagement compared to traditional care approaches.
Healthcare Provider Value: Clinicians reported enhanced ability to monitor patients remotely, identify early warning signs, and coordinate care more effectively.
Feasibility Confirmed: The app-based model proved both technically feasible and clinically valuable across diverse patient demographics.
Impact and Validation
AZIMUTH validated that smartphone-based care could transform outcomes for heart failure patients – a population traditionally challenged by frequent hospitalizations and complex medication regimens. The study proved that digital health solutions, when properly implemented through certified medical device platforms like Healthentia, could enhance both patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
The successful completion of AZIMUTH Phase 1 established a new evidence base for digital health adoption in chronic disease management, demonstrating that collaborative innovation between healthcare institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and technology providers can deliver measurable clinical value. A second paper with results from Phase II is expected soon and new partners have joined efforts in a new study named Azimusa utilizing the Azimuth care model and expanding further the scope to more medical centers in the north with more patients.